Hi, I have implemented .gh analyse in GeometryView and I need before visualization geometry set custom color of result geometry. I cant find right way to set/transform of geometry from .gh script.
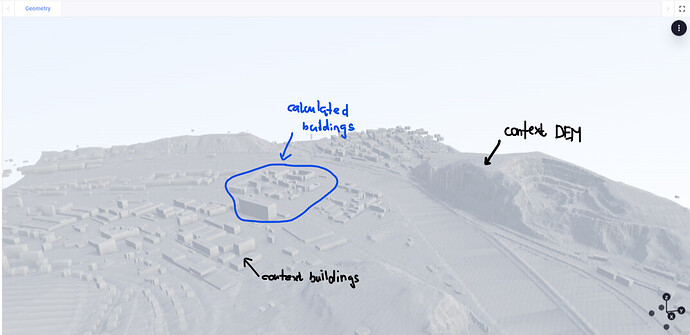
This is my calculated geometry - new buildings:
obj = rhino3dm.CommonObject.Decode(json.loads(output[“values”][0][“InnerTree”][‘{0}’][0][“data”]))
This is context geometry - DEM model and context surrounding buildings:
obj1 = rhino3dm.CommonObject.Decode(json.loads(output[“values”][1][“InnerTree”][‘{0;0}’][0][“data”]))
Geometries are common packed to viktor.File() like this:
file3dm = rhino3dm.File3dm()
file3dm_ext = rhino3dm.File3dm()
file3dm.Objects.Add(obj)
file3dm_ext.Objects.Add(obj)
file3dm_ext.Objects.Add(obj1)
geometry_file = vkt.File()
file3dm.Write(geometry_file.source, version=7)
geometry_file2 = vkt.File()
file3dm_ext.Write(geometry_file2.source, version=7)
My first question is that is it possible to return these geometries via GeometryResult separately, context geometry at once at start application and calculated geometry refreshing by change input parameters?
Second question is, that geometries are in rhino mesh format. I cant find right way to change geometry color e.a. calculated geometry - blue, context geometry - grey or other color. Its needed to convert mesh from rhino to transformable object or something else? Eventually how?
Hi Rick,
thank you for your instructions.
- Im sorry, but I think that I didnt describe my oppinion as well. Every geometry is from .gh deffiniton. But JSON is quite large. It takes over 25 s to show result in DataView window. Of course it depends on data size. 25 000 ms is quite user uncomfortable. In every time is needed to render all geometries, but only calculated geometries (blue - on screen) is change during change parametrization option. But after that is send all geometry of course again at once. It is possible to refresh only calculated geometry, not contextual? By expectation that it helps to respond time. Two JSONs from .gh deffiniton or etc… but it seems that DataView is still refreshes the whole.
- Coloring geometries through Grasshopper component works well. And its not needed to convert geometries in web client. Thx.
Marian
In this case I would use the following setup. It will use memoize, which remembers the result of a function if the inputs don’t change. So only load_surroundings gets run if your lat lon values change, but not if any other parameter changes.
Pseudocode:
@vkt.memoize
def load_surroundings(lat , lon):
grasshopper_script_path = Path(__file__).parent / "load_surroundings_script.gh"
script = vkt.File.from_path(grasshopper_script_path)
input_parameters = {"lat": lat, "lon": lon}
# Run the Grasshopper analysis and obtain the output data
analysis = vkt.grasshopper.GrasshopperAnalysis(script=script, input_parameters=input_parameters)
analysis.execute(timeout=30)
output = analysis.get_output()
# Convert output data to mesh
return json.loads(output["values"][0]["InnerTree"]['{0}'][0]["data"])
class Controller:
@vkt.GeometryView("Buildings with Surroundings", duration_guess=1)
def load_buildings_with_surroundings(self, params, **kwargs):
file3dm = rhino3dm.File3dm()
# Get the surroundings data
surroundings_rhino_file =load_surroundings(params.lat, params.lon)
file3dm.Objects.AddMesh(rhino3dm.CommonObject.Decode(surroundings_rhino_file))
# Run the buildings
grasshopper_script_path = Path(__file__).parent / "buildings.gh"
script = vkt.File.from_path(grasshopper_script_path)
# Run the Grasshopper analysis and obtain the output data
analysis = vkt.grasshopper.GrasshopperAnalysis(script=script, input_parameters=input_parameters)
analysis.execute(timeout=30)
output = analysis.get_output()
# Combine the surroundings with the buildings output
obj = rhino3dm.CommonObject.Decode(json.loads(output["values"][0]["InnerTree"]['{0}'][0]["data"]))
file3dm.Objects.AddMesh(obj)
# Write to geometry_file
geometry_file = vkt.File()
file3dm.Write(geometry_file.source, version=7)
return vkt.GeometryResult(geometry=geometry_file, geometry_type="3dm")
Hi @rvandijk,
thanks a lot for your pseudocode. I implement @vkt.memoize decorator function to my app.py and tested behaviour. I create two .gh deffinitions (1st through memoize with full geometry, 2nd with only computed geometry in output JSON) acording your code.
By first run of analyse appear all geometries, it tooks over 32 032 ms (POST form grasshopper around 11 623 ms, rest of time is spend by parsing and vizualize geometry in DataView).
Second run is used only computed geometry. It tooks depends on parameters settings: 21 198 ms, 24 317 MS. Input data sizing is under 50 MB. It helps me with responses. Area is center of county city aprox. 1 square km. Is there some other ways to compress or influence time responses of application? Do I have standard time responses? I understand that I try to send large data from backend to frontend by network of course. At now we have better imagination about app behavior and data sizing.
Thx,
Marian
Hi @Marian ,
Just to check; parsing the geometry (using rhino_file.Objects.Add(mesh)) takes ± 21 seconds? I think this is standard, and indeed quite expected. Probably your published application will run a bit faster.
In that case, you could also save the rhino_file in Storage, and retrieve it from there. This should skip the parsing as well. In that case, you add a button that does the load_surroundings step, and then have the view load the model from Storage every time.
Some other idea that might be faster, is to join all your meshes in 1 mesh, so you only have to run Add once.
Another idea is to lower the resolution of the context. The mountains are very high resolution. You could check the vertices count for each mesh and determine meshes with high count. Sometimes buildings have rounded corners or such, which also results in high vertices count.
Hopefully that helps